Eczema Treatment
Eczema Treatment Treatment in Bhubaneswar
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes inflammation, dryness, itching, and irritation. It can affect people of all ages, especially children, and often comes in cycles of flare-ups and remissions. While there is no cure, various treatments can control symptoms, prevent flare-ups, and improve the quality of life.
What is Eczema?
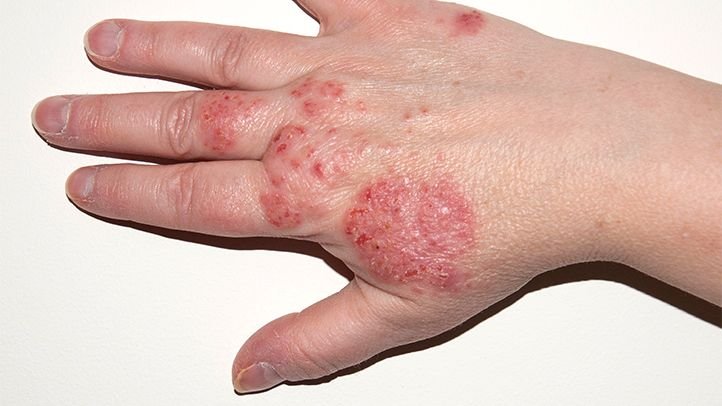
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, red, and cracked skin. It results from a compromised skin barrier that allows allergens, bacteria, and irritants to penetrate the skin easily, triggering inflammation. It may be caused by a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors. Eczema is not contagious but can be distressing, especially when persistent or severe. In many individuals, eczema is associated with other allergic conditions like asthma or hay fever. Proper treatment focuses on hydrating the skin, reducing inflammation, and managing triggers to minimize flares.
Symptoms of Eczema
Intense itching
Red or inflamed patches of skin
Dry, scaly, or cracked skin
Fluid-filled blisters that may ooze and crust over
Thickened, rough skin from long-term scratching
Raw or bleeding areas due to scratching
Common sites: hands, face, neck, elbows, knees, and ankles
Causes of Eczema
Soaps, detergents, and cleaning agents
Wool or synthetic fabrics
Dust, pollen, pet dander
Food allergies (e.g., dairy, nuts, wheat in children)
Changes in temperature or humidity
Stress and emotional strain
Sweat and prolonged heat exposure
Certain fragrances and cosmetics
Eczema Treatments
✅ 1. Skincare & Basic Management
Moisturizers (Emollients)
Applied 2–3 times daily to prevent dryness and restore the skin barrier
Prefer fragrance-free, thick creams or ointments
Gentle Cleansing
Use non-soap cleansers or mild, pH-balanced products
Avoid long, hot showers
Cool Compresses
Soothe itching and inflammation
✅ 2. Topical Medications
Topical Corticosteroids
First-line treatment during flare-ups (e.g., hydrocortisone, betamethasone)
Reduce inflammation, redness, and itching
Use under medical supervision to avoid thinning skin
Calcineurin Inhibitors (e.g., Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus)
Non-steroidal alternatives for sensitive areas (face, eyelids, genitals)
Safe for long-term use in mild to moderate cases
✅ 3. Oral Medications
Antihistamines
Help reduce nighttime itching and improve sleep
May include cetirizine, loratadine, or hydroxyzine
Oral Corticosteroids
Short-term use in severe flare-ups; not for long-term due to side effects
Antibiotics
For secondary bacterial infections in broken or oozing eczema patches
✅ 4. Advanced & Biologic Treatments
Phototherapy (UVB Light Therapy)
Controlled exposure to UVB light reduces inflammation in moderate to severe eczema
Biologic Therapy (Dupilumab)
FDA-approved injectable medication for moderate-to-severe eczema not responsive to conventional treatment
Targets the immune response involved in eczema flares
Immunosuppressants (Cyclosporine, Methotrexate)
Used in severe chronic cases under specialist supervision
✅ 5. Natural Remedies & Supportive Therapies
Oatmeal Baths
Soothes itching and calms inflamed skin
Aloe Vera or Coconut Oil
Natural anti-inflammatory and moisturizing properties
Probiotics & Anti-inflammatory Diet
May support gut-skin connection in eczema-prone individuals (consult your doctor)