Atopic Dermatitis Treatment Treatment
Atopic Dermatitis Treatment in Bhubaneswar
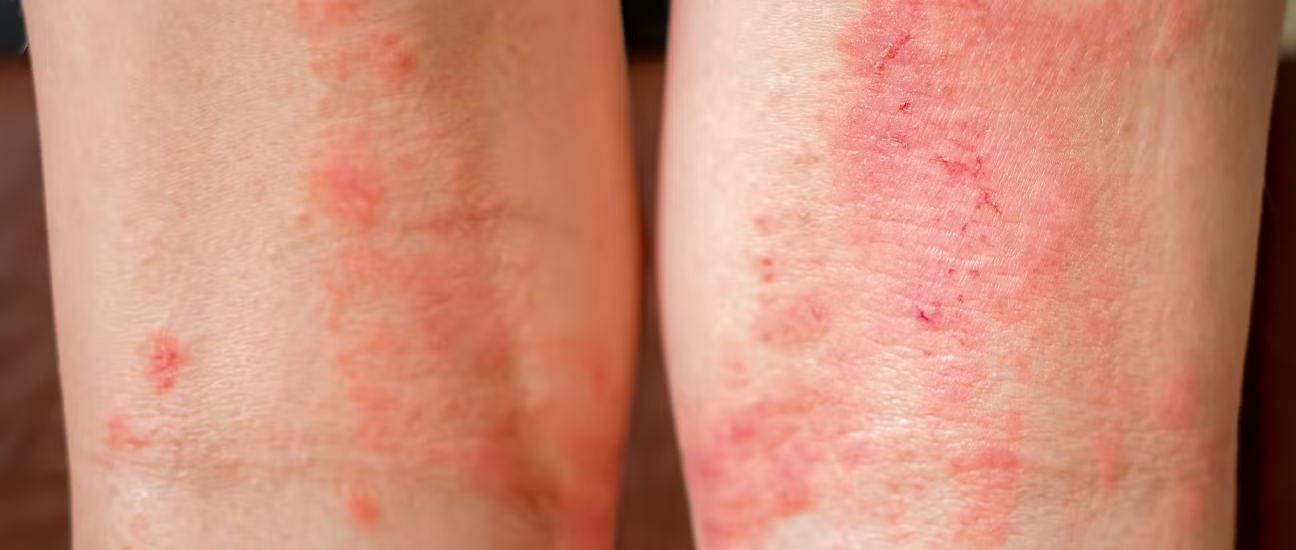
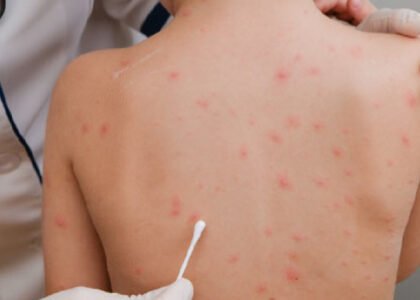
Atopic Dermatitis is the most common form of eczema, a chronic, inflammatory skin disorder that often begins in childhood and may continue into adulthood. It is characterized by intensely itchy, dry, and inflamed skin, with episodes of flare-ups and remissions. Though not contagious, it can significantly affect quality of life if left untreated.
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic Dermatitis (AD) is a chronic immune-mediated skin condition in which the skin becomes dry, red, itchy, and irritated due to a weakened skin barrier and overactive immune response. It is often associated with a personal or family history of asthma, hay fever, or other allergies, making it part of the “atopic triad.” The condition tends to flare up with exposure to allergens, irritants, stress, infections, and climate changes. The skin becomes vulnerable to bacterial infections and may thicken or darken due to constant scratching. While there’s no permanent cure, a combination of skincare management, medical treatment, and lifestyle changes can control the symptoms and prevent flare-ups effectively.
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Severe itching, especially at night
Dry, scaly, and inflamed skin
Red or brownish-gray patches (common on face, neck, arms, legs)
Oozing or crusted blisters during flare-ups
Thickened, cracked skin in chronic cases
Raw or bleeding areas due to scratching
May be associated with allergic rhinitis or asthma
Atopic Dermatitis Treatments
✅ 1. Daily Skincare & Hydration
Moisturizers (Emollients)
Apply liberally at least twice a day, especially after bathing
Choose fragrance-free, thick creams or ointments (e.g., petroleum jelly, ceramide creams)
Gentle Bathing Routine
Use lukewarm water and fragrance-free, non-soap cleansers
Limit baths/showers to 5–10 minutes
Pat skin dry and apply moisturizer immediately
✅ 2. Topical Medications
Topical Corticosteroids
First-line treatment for flare-ups
Reduces inflammation and itching (e.g., hydrocortisone, mometasone)
Use in short courses under medical supervision
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors (Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus)
Non-steroidal, safe for long-term use
Especially effective for sensitive areas (face, neck, eyelids)
Antibiotic Ointments
Used for secondary skin infections caused by scratching (e.g., mupirocin)
✅ 3. Oral Medications
Antihistamines
Reduce nighttime itching and improve sleep (e.g., cetirizine, hydroxyzine)
Oral Corticosteroids
Used in severe flare-ups but not recommended long-term
Immunosuppressants
Cyclosporine, methotrexate, azathioprine – for moderate to severe cases under specialist care
✅ 4. Biologic Therapy
Dupilumab (Dupixent)
FDA-approved injectable biologic for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis
Targets specific immune pathways (IL-4 and IL-13)
Offers long-term control with fewer side effects than steroids
✅ 5. Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
Narrowband UVB Therapy
Safe and effective for widespread or chronic atopic dermatitis
Performed in clinical settings under dermatologist supervision